Allergies can impact your quality of life more than you might realize. From constant sneezing and itchy eyes to unexplained rashes or chronic fatigue, allergic reactions can range from mildly uncomfortable to seriously disruptive. The good news? With accurate allergy testing, it’s possible to pinpoint the exact triggers behind your symptoms and find long-lasting relief through targeted treatment.
Understanding Allergies and Why Testing Matters
An allergy is your immune system’s overreaction to substances that are normally harmless. These substances — known as allergens — can include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, certain foods, insect stings, or even medications. When your immune system detects an allergen, it releases chemicals like histamine, causing inflammation and allergy symptoms.
Common symptoms of allergies include:
- Sneezing and nasal congestion
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Skin rashes or hives
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Digestive issues (after eating certain foods)
- Fatigue or headaches
Because these symptoms can overlap with other conditions like sinus infections, eczema, or asthma, accurate allergy testing is essential. Testing helps determine exactly what’s causing your symptoms, so your treatment plan can be precise and effective.
Types of Allergy Testing
There are several types of allergy tests, and your doctor will recommend the best one depending on your symptoms and medical history. Each test identifies different allergens, whether they come from food, the environment, or contact with your skin.
- Skin Prick Test (SPT)
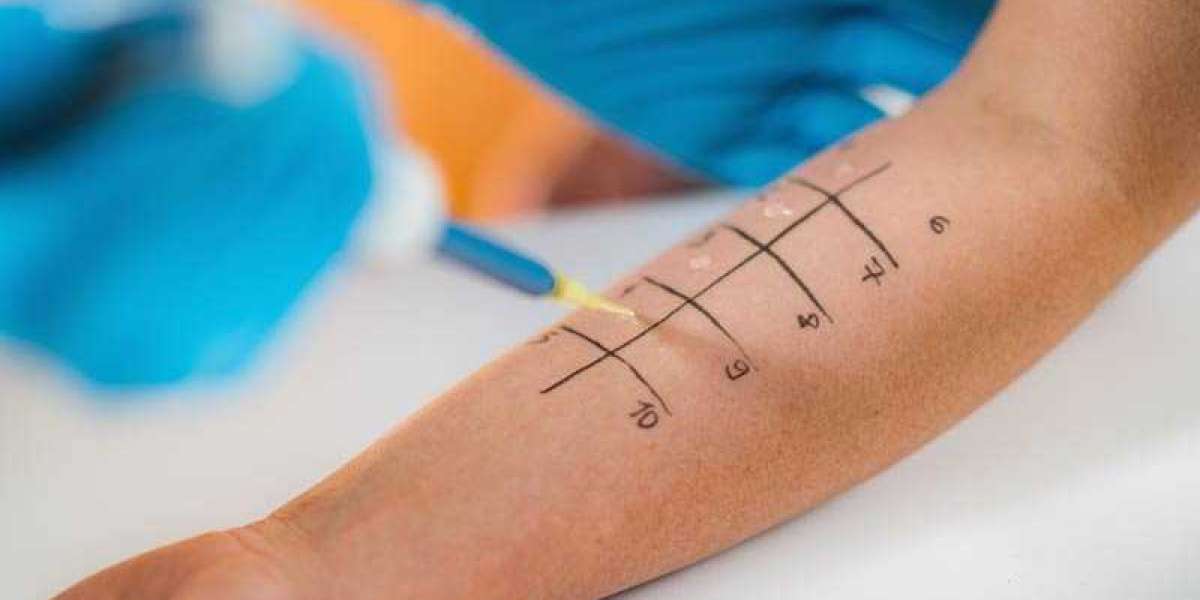
The skin prick test is the most common form of allergy testing. During this test, your provider places tiny drops of various allergens on your skin — usually on your forearm or back — and lightly pricks the surface. If you’re allergic to one of the substances, a small, itchy bump (similar to a mosquito bite) will appear within 15–20 minutes.
This test can detect allergies to:
- Pollen (trees, grasses, and weeds)
- Pet dander
- Dust mites
- Mold spores
- Foods like peanuts, milk, or shellfish
The skin prick test is quick, safe, and provides instant results, making it ideal for identifying multiple allergens in one session.
- Intradermal Test
If your skin prick test results are inconclusive or if your symptoms are severe, your doctor might perform an intradermal test. In this method, a small amount of allergen is injected just beneath the surface of your skin.
This test is more sensitive than a skin prick test and is especially useful for diagnosing insect venom or drug allergies. However, because it can trigger stronger reactions, it’s always performed under medical supervision.
- Blood Test (Specific IgE Test)
For patients who can’t undergo skin testing — such as those with skin conditions or those taking antihistamines — a blood test may be recommended. The ImmunoCAP or RAST test measures the amount of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your blood that respond to specific allergens.
Blood testing can identify a wide range of allergens, including:
- Foods (milk, eggs, nuts, seafood, soy, etc.)
- Environmental triggers (dust mites, mold, pollen)
- Animal dander
Although results take a few days, blood testing is a reliable and less invasive alternative to skin testing.
- Patch Testing
If you experience contact dermatitis — a rash that develops after touching certain substances — your provider may recommend patch testing. Small patches containing potential allergens (like metals, fragrances, or chemicals) are applied to your skin, typically on your back, and left in place for 48 hours.
Your provider checks for delayed reactions to identify what substances are causing your skin irritation.
Preparing for an Allergy Test
Before undergoing allergy testing, there are a few important steps to ensure accurate results:
- Avoid antihistamines for at least 3–5 days before testing, as they can suppress reactions.
- Discuss medications you’re currently taking — some may interfere with results.
- Inform your doctor of any recent allergic reactions or illnesses.
- Wear comfortable clothing if skin testing is planned, as your arms or back will need to be exposed.
Your provider will review your medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle to determine which type of test is most suitable for you.
What to Expect During and After the Test
Most allergy tests are quick and virtually painless. During a skin prick test, for example, you’ll likely feel a mild tingling or itching sensation where the allergen is applied. If a reaction occurs, the area may swell slightly, but this usually fades within a few hours.
After testing, your provider will discuss the results with you. Each allergen tested will be rated based on how strong your reaction was. From there, you’ll receive a personalized treatment plan, which may include:
- Allergen avoidance strategies (reducing exposure to triggers)
- Medications like antihistamines, nasal sprays, or eye drops
- Allergy shots (immunotherapy) for long-term desensitization
- Lifestyle adjustments to improve symptom management
Benefits of Allergy Testing
Accurate allergy testing offers numerous health benefits beyond symptom relief. Here’s how it can improve your overall well-being:
- Precise Diagnosis: Identifies the exact substances causing allergic reactions.
- Targeted Treatment: Enables your doctor to develop a personalized care plan.
- Improved Quality of Life: Reduces or eliminates chronic symptoms like congestion, fatigue, and skin irritation.
- Prevention of Severe Reactions: Helps you avoid allergens that could trigger life-threatening responses.
- Better Control Over Chronic Conditions: Supports management of related issues such as asthma, eczema, or sinusitis.
Who Should Get Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing is recommended for anyone experiencing recurring or unexplained symptoms such as:
- Persistent sneezing or congestion
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Unexplained rashes or eczema
- Food-related digestive issues
- Asthma or breathing difficulties
It’s also helpful for individuals who have seasonal allergies or want to determine if environmental factors are worsening their existing health conditions.
Children can also benefit from allergy testing, as early diagnosis helps prevent chronic symptoms and improves their comfort and development.
The Path to Relief: Managing Allergies After Testing
Once your allergens have been identified, you can begin an effective treatment plan. The most common long-term approach is allergy immunotherapy, which involves exposing your body to small, controlled doses of allergens to build tolerance over time. This process can dramatically reduce or even eliminate allergic responses.
Additionally, simple lifestyle modifications — such as using air purifiers, keeping pets out of bedrooms, or avoiding certain foods — can make a big difference in reducing daily symptoms.
Final Thoughts
If allergies are interfering with your daily life, accurate allergy testing is the first step toward lasting relief. Understanding exactly what triggers your symptoms allows you and your healthcare provider to create a targeted plan for prevention, treatment, and long-term comfort.