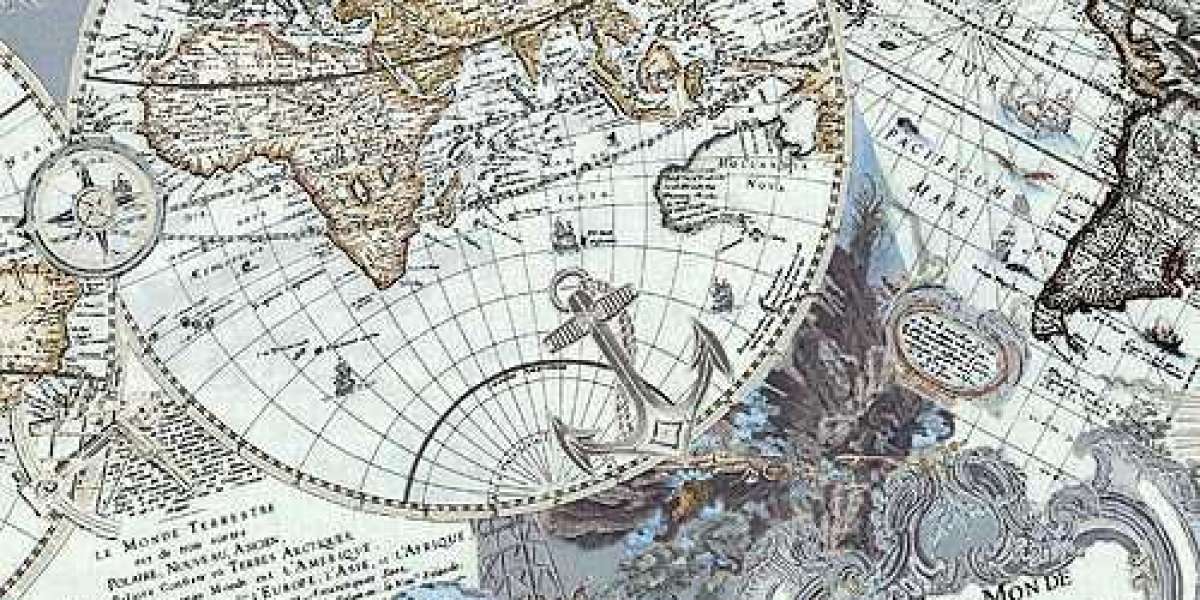
Antique city maps are more than just visual representations of geography; they are time capsules that preserve the cultural, political, and social identity of a bygone era. From medieval engravings to Renaissance cartography, each city map tells a story about how urban centers evolved, how empires rose and fell, and how artists and explorers interpreted the world around them. Today, antique city maps are admired not only by historians but also by collectors, decorators, and anyone captivated by the beauty of historical art.
The Origins of City Mapping
The practice of creating maps dates back thousands of years, but the creation of detailed city maps began to flourish during the medieval and Renaissance periods. As trade expanded and exploration intensified, cities became hubs of commerce and culture, necessitating detailed layouts for travelers, merchants, and rulers. Early maps were often symbolic rather than accurate, reflecting spiritual beliefs, landmarks, and mythological elements alongside the actual streets and districts.
The Renaissance and the Golden Age of Mapping
The Renaissance period marked a turning point in the accuracy and artistry of maps. Cities such as Venice, Florence, Paris, and London began to appear in beautifully detailed maps that balanced science and artistry. Cartographers like Sebastian Münster and Braun Hogenberg produced magnificent city views that not only depicted buildings and streets but also highlighted the vibrancy of city life. These maps were often hand-colored, turning them into decorative masterpieces treasured by nobility and scholars.
The Role of Exploration and Trade
Exploration during the Age of Discovery had a profound influence on city mapping. As explorers charted new lands, ports and cities became focal points for navigation and commerce. Maps of cities like Amsterdam, Lisbon, and Antwerp reflected their role as bustling trade centers. These maps included harbors, shipyards, and bustling marketplaces, offering invaluable insights into the economic importance of these cities. Antique city maps from this era are often filled with ships, trade routes, and elaborate borders that celebrated exploration.
Artistic Flourishes in Antique Maps
What sets antique city maps apart from modern ones is their artistic quality. They were not just tools for navigation but also works of art. Maps frequently included decorative borders, elaborate cartouches, mythical creatures, and detailed illustrations of city landmarks. Engravers worked tirelessly to produce visually appealing maps that reflected the grandeur of the cities they depicted. The artistry of antique city maps has made them highly desirable for collectors and interior decorators, who appreciate their blend of utility and beauty.
Maps as Symbols of Power and Prestige
In many cases, antique city maps were commissioned to showcase political dominance and cultural superiority. Kings, emperors, and wealthy merchants used maps as symbols of prestige. A grandly detailed map of a city often served as a statement of wealth and influence. Cities themselves also used maps as promotional tools, showcasing their size, defenses, and attractions to visitors and potential settlers. Some maps highlighted fortifications, cathedrals, and marketplaces to display the prosperity and importance of the city.
Iconic Antique City Maps
Several antique city maps have achieved legendary status due to their historical significance and visual appeal. The “Nuremberg Chronicle” published in 1493, for example, includes some of the earliest printed city views. Braun Hogenberg’s Civitates Orbis Terrarum, a monumental collection of city maps published between 1572 and 1617, remains one of the most iconic works of cartography. These volumes contained hundreds of city views, capturing the essence of European cities and beyond during the Renaissance. Each map was more than a geographic record; it was a cultural snapshot of urban life.
Collecting Antique City Maps
Today, antique city maps are highly sought after by collectors. Their value depends on factors such as rarity, age, condition, artistic detail, and historical importance. Maps created by renowned cartographers or published in famous atlases command higher prices. Collectors are drawn not only to the visual beauty but also to the sense of history these maps convey. Owning an antique city map is like holding a fragment of history—a tangible connection to the streets, buildings, and lives of people centuries ago.
Decorative Value of Antique Maps
Beyond the realm of collecting, antique city maps have become popular as decorative pieces. Their intricate details and aged charm make them ideal for framing and displaying in homes, offices, and galleries. Interior designers often incorporate antique maps into décor to create a sense of sophistication and timelessness. Whether hung in a study, a library, or a living room, antique city maps transform a space with their historical depth and artistic flair.
Preservation of Antique City Maps
Because of their age and fragility, antique maps require careful preservation. Exposure to sunlight, moisture, or poor storage can cause fading, tearing, and deterioration. Collectors and museums often invest in professional conservation to ensure the longevity of these treasures. Proper framing with acid-free materials, controlled humidity, and protective coverings are essential steps in maintaining their condition. Preservation not only safeguards financial value but also ensures that these historical artifacts continue to be appreciated by future generations.
Academic and Historical Significance
Antique city maps are invaluable resources for researchers and historians. They reveal details about city planning, architecture, and cultural practices of the past. For example, maps of medieval cities often highlight walls, gates, and fortifications, reflecting the importance of defense during turbulent times. Maps from the Enlightenment era, on the other hand, reveal the growing emphasis on science, order, and rationality in city planning. Studying these maps allows historians to reconstruct urban environments and gain deeper insights into the development of civilization.
The Global Spread of City Maps
While Europe played a central role in the development of city maps, other parts of the world also produced extraordinary works. Chinese city maps, for instance, were highly detailed and often incorporated elements of cosmology and Feng Shui. Japanese maps of cities such as Edo (modern-day Tokyo) depicted the intricate networks of streets, temples, and waterways. In the Islamic world, city maps were often tied to religious pilgrimage routes, particularly those depicting Mecca and other holy cities. The diversity of cartographic traditions highlights the universal human desire to record and understand urban spaces.
The Shift Toward Modern Mapping
With the advent of modern technology, mapping became more precise, standardized, and functional. By the 19th century, maps increasingly focused on accuracy and practical utility rather than artistic decoration. While modern maps are crucial for navigation and planning, they often lack the artistic soul of antique maps. This shift has only increased the appreciation of antique city maps as unique works of art from a time when craftsmanship and creativity were inseparable from cartography.
The Market for Antique City Maps
The market for antique city maps continues to thrive, fueled by collectors, investors, and enthusiasts of history and art. Auction houses, galleries, and specialized dealers frequently feature rare maps, and prices can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on the rarity and significance of the piece. Online platforms have also made antique maps more accessible, allowing global buyers to discover and acquire them. The continued interest reflects a growing recognition of maps not just as tools, but as historical artifacts that bridge art and knowledge.
Antique Maps in the Digital Age
Interestingly, the digital era has not diminished the fascination with antique maps; instead, it has amplified their relevance. Many museums and libraries have digitized their collections, making high-resolution images of antique maps accessible to the public worldwide. Digital archives allow researchers, educators, and enthusiasts to study maps in detail without handling fragile originals. At the same time, the tactile experience of owning and displaying an authentic antique city map remains irreplaceable, preserving the allure of physical artifacts.
Why Antique City Maps Still Captivate Us
Antique city maps captivate modern audiences because they embody both precision and imagination. They reveal how people of the past perceived their cities, blending practical detail with symbolic elements. Each map is a narrative that captures the spirit of its time, offering insights into commerce, religion, politics, and daily life. They appeal to our curiosity about history while also satisfying our appreciation for artistic beauty. In a fast-paced digital world, antique city maps remind us of the enduring importance of craftsmanship and storytelling.
Conclusion: A Timeless Journey Through History
Antique city maps are not merely remnants of the past; they are treasures that continue to inspire curiosity, admiration, and reflection. They connect us to the ways cities were envisioned centuries ago, preserving stories that might otherwise be lost to time. Whether valued for their historical insight, artistic merit, or decorative elegance, these maps hold a timeless appeal. For collectors, historians, or admirers of beauty, antique city maps are more than just objects—they are windows into history, offering us a chance to trace the footsteps of civilization across centuries and continents.